Research
Distracted Practice
Patient Safety is a serious global public health concern. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), there is a 1 in a million chance of a person being harmed while traveling by plane. In comparison, there is a 1 in 300 chance of a patient being harmed during health care. An estimated 66 million potentially significant errors occur per year in the United Kingdom (UK). 237 million medication errors occur at some point in the medication process in England per year.
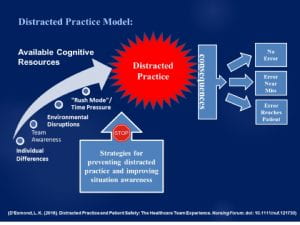
Distracted Practice is the diversion of a portion of available cognitive resources that may be needed to effectively perform/carry out the current practice activity.
The experience of distracted practice is the result of limited cognitive resources.
Distracted Practice:
- Is dynamic, temporary and may be only momentary
- Varies by individual and fluctuates day to day
- Continually changes throughout the day, depending on the workload and level of distractions
- An individual may or may not be aware of the stimulus
- Causes an individual to shift into “automatic mode” where they are no longer thinking critically
This is when errors occur. Increasing awareness of distracted practice is important to prevent or reduce errors that affect patient safety.